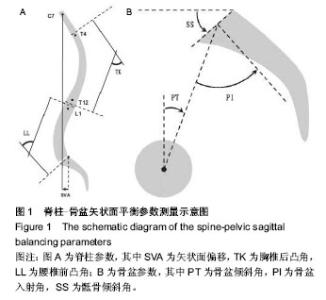
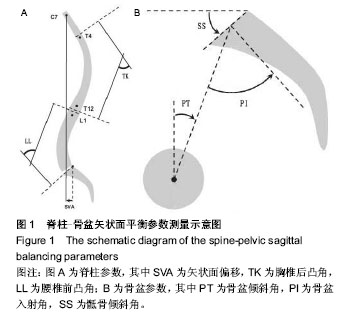
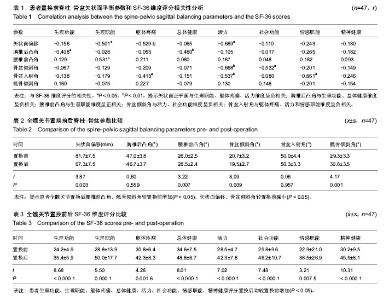
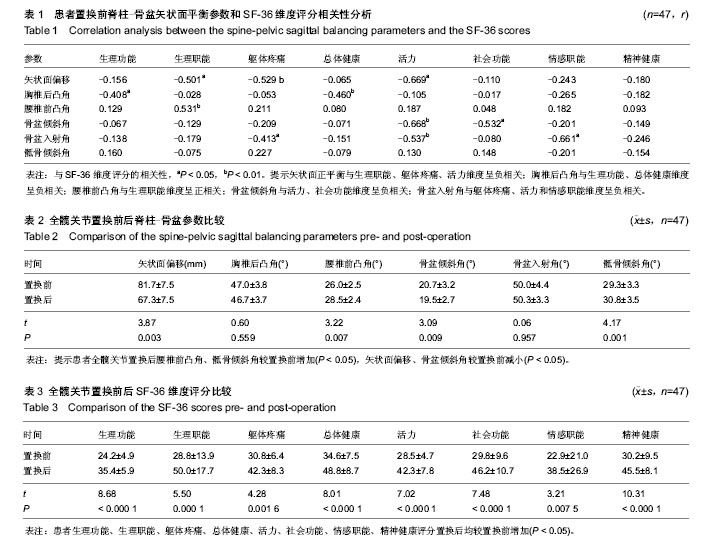
| [1] 游浩,程翠年,张卉,等.强直性脊柱炎病因及其发病机制的研究进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2012,20(9):77-79.
[2] 王斌.强直性脊柱炎影像学分析[J].中国CT和MRI杂志, 2014, 12(3):97-99.
[3] 李静.强直性脊柱炎的临床治疗策略与研究进展[J].中国疗养医学,2014,23(9):782-785.
[4] 张亮,徐辉,郭晓忠,等.人工全髋关节置换术治疗强直性脊柱炎的中期疗效[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,28(1):1-6.
[5] 胡如印,田晓滨,孙立,等.人工全髋关节置换治疗强直性脊柱炎髋关节强直畸形[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(44): 8356-8360.
[6] 边焱焱,翁习生,林进,等.多关节置换治疗晚期下肢关节疾患[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(3):296-299.
[7] 曾勇,何睿,李庆,等.脊柱截骨并人工全髋关节置换术治疗强直性脊柱炎后凸畸形并髋关节重度屈曲挛缩畸形[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,28(8):942-946.
[8] 宋若先,张永刚.强直性脊柱炎后凸畸形矫形修复中截骨方法的进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(17):3218-3222.
[9] 王晓平,陆明,马华松,等.椎弓根螺钉内固定强直性脊柱炎后凸畸形:病例及文献分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(35): 6599-6606.
[10] 付振栋.THA治疗强直性脊柱炎的临床体会[J].中国现代药物应用,2014,8(20): 63-64.
[11] 陈涛,黎观保,梁科友,等.脊柱-骨盆矢状面平衡及其在脊柱疾病治疗中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(13): 2423-2430.
[12] 徐斌,瞿玉兴.基于骨盆投射角法的骨盆矢状位平衡研究进展[J].海南医学院学报,2010,16(2):248-250.
[13] 米尔萨力江•亚森,费琴明.骨盆参数及其临床意义[J].国际骨科学杂志,2010,31(4):210-213.
[14] 王太平,郑召民,刘辉,等.成人脊柱畸形矢状面平衡与生存质量的相关性分析[J].中华医学杂志,2012,92(21):1481-1485.
[15] 陈宗霖,夏磊.脊柱侧弯患者术前术后骨盆矢状位参数分析[J].河南医学研究,2012,21(1):29-31.
[16] 李危石,陈仲强,Kirkham B Wood. 成人特发性脊柱侧凸患者脊柱-骨盆矢状位平衡分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(3): 207-211.
[17] 徐宝山,Le Huec Jean-Gharles,夏群.内镜辅助微创入路人工腰椎间盘置换术的临床效果及矢状平衡分析[J].中华骨科杂志, 2008,28(8):622-627.
[18] Lafage V, Schwab F, Skalli W, et al. Standing balance and sagittal plane spinal deformity: analysis of spinopelvic and gravity line parameters. Spine. 2008;33(14): 1572-1578.
[19] 朱泽章.骨盆投射角在成人脊柱畸形临床评估中的应用价值[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(3):199-200.
[20] Blondel B,Jouve JL,Panuel M,et al. Pelvic incidence reliability in spine sagittal balance.Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot.2008;94(4):321-326.
[21] Qian BP, Wang XH, Qiu Y, et al. The influence of closing-opening wedge osteotomy on sagittal balance in thoracolumbar kyphosis sencondary to ankylosing spondylitis:a comparison with closing wedge osteotomy. Spine. 2012;37(16):1415-1423.
[22] Mac-Thiong JM, Berthonnaud É, Dimar JR, et al. Sagittal alignment of the spine and pelvis during growth. Spine. 2004;29(15):1642-1647.
[23] Lafage V, Schwab F, Patel A, et al. Pelvic tilt and truncal inclination: two key radiographic parameters in the setting of adults with spinal deformity. Spine. 2009;34(17): 599-606.
[24] 李伟杰.全髋关节置换术对强直性脊柱炎累及髋关节患者脊柱-骨盆关系的影响[D].广州中医药大学, 2011.
[25] Glassman SD, Bridwell K, Dimar JR, et al. The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity. Spine. 2005;30(18): 2024-2029.
[26] Gottfried ON, Daubs MD, Patel AA, et al. Spinopelvic parameters in postfusion flatback deformity patients. Spine J. 2009;9(8):639-647.
[27] Glassman S, Berven S, Bridwell K, et al. Correlation of radiographic parameters and clinical symptoms in adult scoliosis. Spine. 2005;30(6):682-688.
[28] 徐宝山,马信龙.脊柱骨盆矢状力线在脊柱疾患中的意义[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(1):80-85.
[29] Vaz G, Roussouly P, Berthonnaud E, et al. Sagittal morphology and equilibrium of pelvis and spine. Eur Spine J. 2002;11(1):80-87.
[30] Husson JL, Mallet JF, Huten D, et al. The lumbar-pelvic- femoral complex: applications in hip pathology Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2010; 96(4) Suppl:10-16.
[31] Tang WM, Chiu KY. Primary total hip arthroplasty in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15 (1):52-58.
[32] 陈立民,赵承斌,姚猛,等.脊椎楔形截骨加全髋置换术矫治强直性脊柱炎后凸及髋关节强直[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2009,19(4): 264-267.
[33] Morvan G, Wybier M, Mathieu P,et al. Plain radiographs of the spine: static and relationships between spine and pelvis. J Radiol. 2008; 89:654-666.
[34] 郑召民.应重视脊柱-骨盆矢状面平衡是脊柱畸形手术治疗中的作用[J].中华医学杂志, 2013, 93(7):481-482. |